3. Buttons in Tkinter
By Bernd Klein. Last modified: 01 Feb 2022.
Tkinter Buttons
The Button widget is a standard Tkinter widget, which is used for various kinds of buttons. A button is a widget which is designed for the user to interact with, i.e. if the button is pressed by mouse click some action might be started. They can also contain text and images like labels. While labels can display text in various fonts, a button can only display text in a single font. The text of a button can span more than one line.
A Python function or method can be associated with a button. This function or method will be executed, if the button is pressed in some way.
Live Python training
Example for the Button Class
The following script defines two buttons: one to quit the application and another one for the action, i.e. printing the text "Tkinter is easy to use!" on the terminal.
import tkinter as tk
def write_slogan():
print("Tkinter is easy to use!")
root = tk.Tk()
frame = tk.Frame(root)
frame.pack()
button = tk.Button(frame,
text="QUIT",
fg="red",
command=quit)
button.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
slogan = tk.Button(frame,
text="Hello",
command=write_slogan)
slogan.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
root.mainloop()
The result of the previous example looks like this:
Dynamical Content in a Label
The following script shows an example, where a label is dynamically incremented by 1 until a stop button is pressed:
import tkinter as tk
counter = 0
def counter_label(label):
counter = 0
def count():
global counter
counter += 1
label.config(text=str(counter))
label.after(1000, count)
count()
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Counting Seconds")
label = tk.Label(root, fg="dark green")
label.pack()
counter_label(label)
button = tk.Button(root, text='Stop', width=25, command=root.destroy)
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
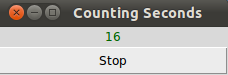
The result of the previous example looks like this:
Live Python training
Upcoming online Courses
10 Mar 2025 to 14 Mar 2025
07 Apr 2025 to 11 Apr 2025
23 Jun 2025 to 27 Jun 2025
28 Jul 2025 to 01 Aug 2025
Efficient Data Analysis with Pandas
10 Mar 2025 to 11 Mar 2025
07 Apr 2025 to 08 Apr 2025
02 Jun 2025 to 03 Jun 2025
23 Jun 2025 to 24 Jun 2025
28 Jul 2025 to 29 Jul 2025
09 Apr 2025 to 11 Apr 2025
04 Jun 2025 to 06 Jun 2025
Python and Machine Learning Course
10 Mar 2025 to 14 Mar 2025
07 Apr 2025 to 11 Apr 2025
02 Jun 2025 to 06 Jun 2025
28 Jul 2025 to 01 Aug 2025
Deep Learning for Computer Vision (5 days)
10 Mar 2025 to 14 Mar 2025
07 Apr 2025 to 11 Apr 2025
02 Jun 2025 to 06 Jun 2025
28 Jul 2025 to 01 Aug 2025
